The Hidden Risk in M&A Deals
Why Overlooking Cybersecurity Could Cost Millions in Your Next Acquisition

Cybersecurity due diligence has become a cornerstone of any successful merger and acquisition (M&A) deal. With the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, data, and technology, any oversight in this area can result in substantial financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. In the following we will unpack why cybersecurity due diligence is critical in M&A transactions, the risks of neglecting it, and a practical roadmap to ensure compliance and safeguard value during the deal.
When companies enter an M&A transaction, they typically focus on financial, operational, and market factors. However, overlooking the cybersecurity posture of the target company can lead to devastating outcomes. Think of it like buying a car—you don’t just look at the shiny exterior; you need to check under the hood to make sure it runs smoothly. The same principle applies here. A company's cybersecurity vulnerabilities can impact its valuation, expose the acquirer to inherited risks, and even derail the deal entirely.
Cybersecurity risks in M&A can take many forms. These include unpatched vulnerabilities, outdated systems, or third-party dependencies that could open the door to breaches. Another common issue is poor data governance. If the target company cannot demonstrate clear data ownership or has a history of mishandling sensitive information, it could lead to regulatory penalties or lawsuits. Moreover, cyberattacks often go unnoticed for months, meaning a company could already be compromised without realizing it. Acquiring such a business without addressing these risks is akin to buying a ticking time bomb.
For example, in 2017, Verizon’s acquisition of Yahoo highlighted the importance of cybersecurity due diligence. Midway through the deal, Yahoo disclosed two massive data breaches affecting billions of users. This revelation forced Verizon to renegotiate the purchase price, ultimately reducing it by $350 million. This case underscores how cybersecurity issues can materially affect deal terms, valuation, and post-acquisition integration.
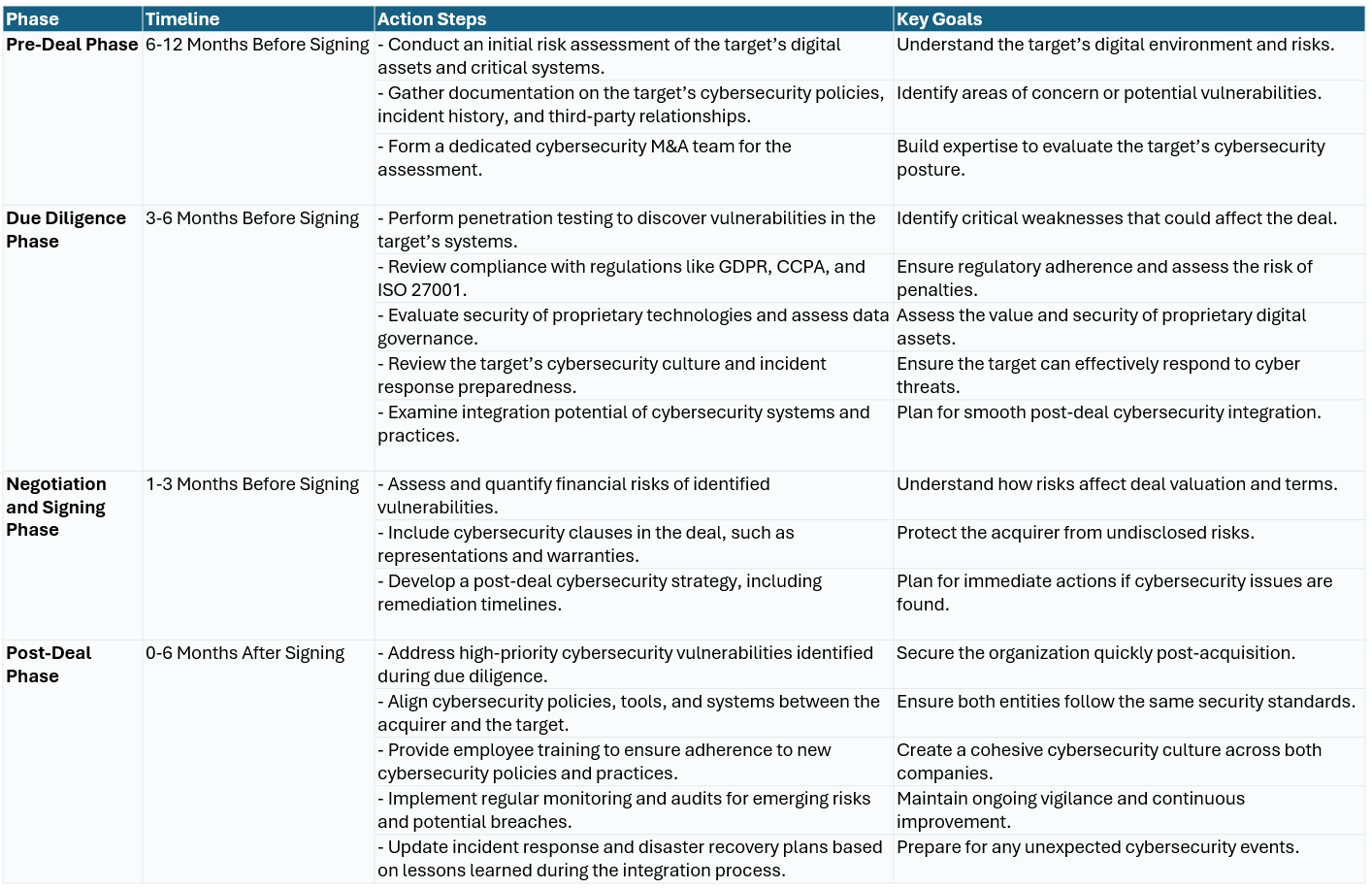
To mitigate these risks, cybersecurity due diligence should be embedded as a critical part of the M&A process. Here’s a step-by-step timetable and playbook for achieving compliance:
Pre-Deal Phase (6-12 Months Before Signing)
Initial Risk Assessment
Begin by identifying the target company's key digital assets, such as intellectual property, customer data, and critical systems, which are vital to its operations and value. Assess the potential impact of a cybersecurity incident on these assets, considering potential financial losses, regulatory implications, and reputational damage. This evaluation should include understanding existing vulnerabilities and the likelihood of exploitation. To ensure a thorough and effective process, form a dedicated team with expertise in cybersecurity and mergers and acquisitions. This team will lead the assessment, providing actionable insights and helping to address any identified risks during the transaction process.
Information Gathering
Request comprehensive documentation detailing the target’s cybersecurity policies, procedures, and infrastructure to understand the framework protecting its digital assets. Examine relationships with third-party vendors, especially those with access to sensitive systems, to identify potential external vulnerabilities. Investigate any past cybersecurity incidents, including the nature of the breaches, how they were managed, and the outcomes of the response efforts. This evaluation provides insight into the target’s resilience and readiness to handle threats, as well as any potential risks associated with its external partnerships or historical weaknesses in its cybersecurity posture.
Due Diligence Phase (3-6 Months Before Signing)
Perform an in-depth technical assessment to evaluate the target’s cybersecurity posture. Conduct penetration testing to uncover vulnerabilities within the target’s systems that could be exploited. Audit the organization’s compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, as well as adherence to industry standards like ISO 27001. Additionally, assess the security of proprietary technologies or software to ensure they meet best practices and do not pose hidden risks. This thorough evaluation helps identify weaknesses, ensures regulatory alignment, and protects the value of unique technological assets in the context of the transaction.
Cultural and Procedural Review
Assess the target company's efforts to foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness among employees, ensuring they understand and adhere to best practices. Evaluate the robustness of incident response plans, backup protocols, and disaster recovery capabilities to determine their effectiveness in mitigating and recovering from potential threats. Additionally, review how well the target's cybersecurity policies align with the acquiring company's standards to identify any gaps or areas requiring integration. This comprehensive analysis ensures that both cultural and operational aspects of cybersecurity are compatible and resilient during and after the acquisition process.
Integration Readiness
Analyze the compatibility of the target’s systems and processes with those of the acquiring company to ensure seamless integration. Identify any gaps in cybersecurity policies, tools, or practices that could hinder alignment between the two organizations. Propose remediation strategies to address these discrepancies and create a unified cybersecurity posture that supports the merged entity’s operations and protects its digital assets. This process ensures a smooth transition while minimizing potential risks associated with differences in security approaches and infrastructure.
Negotiation and Signing Phase (1-3 Months Before Signing)
Risk Valuation
Quantify the financial risks associated with identified cybersecurity vulnerabilities to understand their potential impact on the transaction. Incorporate these risks into the purchase price or structure escrow agreements to mitigate potential losses. Include robust representations and warranties clauses in the deal to safeguard the acquiring company against any undisclosed cybersecurity issues. These measures provide a financial and legal buffer, ensuring greater transparency and reducing exposure to unexpected liabilities arising from cybersecurity shortcomings.
Deal Structuring
Develop a risk mitigation strategy to address identified cybersecurity issues, which may include requiring the target to complete specific remediation efforts before closing the deal. Incorporate clear and enforceable cybersecurity requirements within the transition services agreement (TSA) to ensure both parties maintain a strong security posture during the integration period. These measures help protect critical systems and data while minimizing risks during the transition and ensuring compliance with agreed-upon security standards.
Post-Deal Phase (0-6 Months After Signing)
Immediate Risk Mitigation
Address high-priority vulnerabilities uncovered during the due diligence process to mitigate immediate risks to the organization. Implement interim security measures to safeguard critical systems and data throughout the integration phase, ensuring protection against potential threats. These actions help maintain operational stability and secure the transaction while longer-term solutions are developed and deployed.
System Integration and Policy Alignment
Harmonize cybersecurity policies, tools, and standards between both organizations to create a cohesive and secure environment post-acquisition. Provide targeted training for employees of the acquired company to ensure they understand and adhere to the acquiring organization’s cybersecurity expectations. This approach fosters a unified security culture while reducing risks associated with misaligned practices or lack of awareness during the integration process.
Ongoing Monitoring and Improvement
Conduct regular audits to identify emerging risks and address them proactively. Continuously monitor for potential signs of data breaches or unauthorized access to ensure the security of critical systems and data. Update incident response plans based on lessons learned from integration challenges, refining processes to better handle future threats. These actions help maintain an ongoing focus on security and strengthen the organization’s ability to respond effectively to evolving risks post-acquisition.
The Bottom Line
It’s worth noting that cybersecurity due diligence is not just about protecting the acquirer—it also adds value to the deal. A company with strong cybersecurity measures is often more attractive to potential buyers. On the flip side, demonstrating due diligence and proactive risk management can increase confidence among stakeholders, including regulators, investors, and customers.
In today’s interconnected world, ignoring cybersecurity in M&A deals is no longer an option. By embedding these considerations into every phase of the transaction, companies can not only protect themselves from hidden risks but also build stronger, more resilient organizations. The stakes are high, but
with the right approach, cybersecurity due diligence can transform potential liabilities into strategic advantages.