Managing Agentic AI Responsibly
Balancing Autonomy With Corporate Accountability
Agentic AI represents a paradigm shift, enabling autonomous systems capable of decision-making and task execution without continuous human oversight. This transformative technology holds substantial potential, but its adoption also raises critical ethical, governance, and risk management questions that CISOs and management boards must address proactively.
Those systems are designed to operate with greater independence than traditional AI models. They excel in scenarios requiring rapid adaptability, self-learning, and minimal human intervention. These systems can dynamically interpret objectives, explore solutions, and execute actions to meet predefined goals. Examples include self-driving vehicles, advanced manufacturing robots, and autonomous financial trading algorithms.
Ethical Considerations
A fundamental challenge of agentic AI lies in determining responsibility when these systems make harmful decisions. Traditional AI models rely on human-controlled parameters, but agentic AI’s autonomous nature complicates assigning blame. Transparent decision-making processes and audit trails are essential to address this concern.
Without proper oversight, agentic AI can perpetuate or amplify biases. Models trained on biased data sets may produce discriminatory outcomes, undermining public trust and leading to reputational and legal risks. Regular audits and bias mitigation strategies must be integral to system design.
Striking a balance between granting AI autonomy and maintaining oversight is crucial. Excessive independence can lead to unintended consequences, while overregulation may stifle innovation. Boards need clear frameworks outlining where human intervention is necessary.
Governance Strategies
To manage agentic AI effectively, organizations should implement robust governance frameworks tailored to its unique challenges:
1. Define Clear Policies and Objectives: Governance begins with establishing clear guidelines for agentic AI use. Policies should define acceptable applications, risk thresholds, and performance metrics. Objectives must align with broader organizational values, emphasizing safety, fairness, and ethical practices.
2. Integrated Oversight Structures: Assigning responsibility for AI oversight is vital. Boards should empower AI ethics committees or appoint AI-specific officers to monitor deployment and adherence to governance policies.
3. Risk Management Frameworks: Risk management should incorporate comprehensive assessments of AI’s technical, operational, and reputational risks. These assessments must account for agentic AI’s potential for unexpected outcomes and adapt over time to evolving threats.
4. Collaboration with Regulators: As governments introduce AI-specific regulations, proactive engagement with regulatory bodies can ensure compliance and influence policy development. Staying ahead of regulatory trends minimizes legal and financial liabilities.
Business Risks of Agentic AI
The deployment of agentic AI presents several risks that boards must carefully weigh:
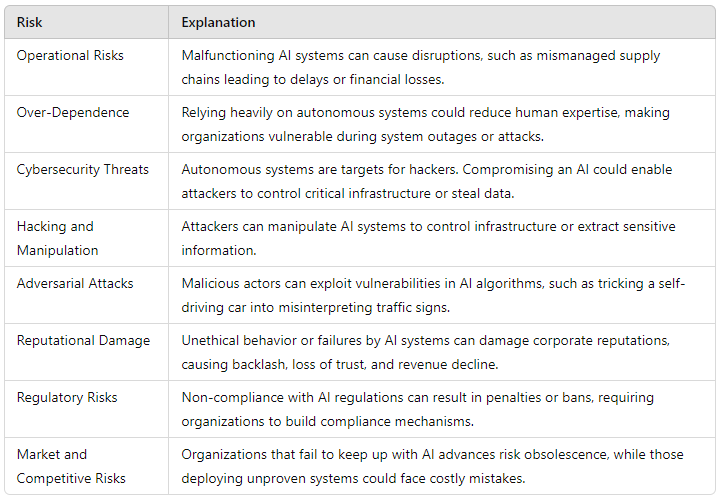
1. Operational Risks: Failure Scenarios: Malfunctioning AI systems can cause operational disruptions. For example, an agentic AI in logistics might mismanage supply chains, leading to delays or financial losses.
Over-Dependence: Relying heavily on autonomous systems could erode human expertise, leaving organizations vulnerable during system outages or attacks.
2. Cybersecurity Threats: Hacking and Manipulation: Autonomous systems are attractive targets for hackers. Compromising an agentic AI could enable attackers to control critical infrastructure or steal sensitive data. But also adversarial Attacks might occur, where malicious actors can exploit vulnerabilities in AI algorithms to manipulate outputs, such as tricking a self-driving car into misinterpreting traffic signs.
3. Reputational Damage: Unethical behavior by agentic AI systems can damage corporate reputations. Publicized failures or discriminatory actions by autonomous systems could lead to backlash, loss of trust, and revenue decline.
4. Regulatory Risks: Non-compliance with emerging AI regulations can result in penalties or bans. As regulatory scrutiny increases, organizations must anticipate legal requirements and build compliance mechanisms into their systems.
5. Market and Competitive Risks: Rapid Technological Shifts: Organizations failing to keep pace with advances in agentic AI risk obsolescence. Conversely, deploying unproven systems too quickly could lead to costly mistakes.
Practical Recommendations for CISOs and Boards
To harness agentic AI effectively while mitigating risks, boards and CISOs should adopt these strategies:
1. Conduct Comprehensive Risk Assessments: Evaluate the implications of agentic AI deployments across business functions. Assess potential scenarios, including worst-case outcomes, and build contingency plans accordingly.
2. Invest in Explainable AI: Adopt explainability tools that enable stakeholders to understand how agentic AI reaches its decisions. This transparency fosters trust and aids regulatory compliance.
3. Strengthen Cybersecurity: Implement robust security measures tailored to autonomous systems, such as encryption, real-time monitoring, and anomaly detection. Conduct penetration testing and adversarial attack simulations to uncover vulnerabilities.
4. Enhance Training and Awareness: Educate employees and leadership on the ethical, operational, and legal aspects of agentic AI. Ensure that teams have the skills to manage these systems effectively.
5. Engage in Continuous Monitoring: Autonomous systems require ongoing oversight to ensure they operate within acceptable boundaries. Regular performance evaluations and updates are necessary to address emerging risks.
Closing Thoughts
Agentic AI has the potential to revolutionize industries by driving efficiency, innovation, and resilience. However, its deployment must be guided by strong ethical principles, transparent governance frameworks, and rigorous risk management. For CISOs and boards, understanding the broader implications of agentic AI is not just a matter of technological competence—it is a strategic imperative for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.


Great points. We used to worry about service accounts and service but AI agents are going to be a game-changer when it comes to attack surfaces
thanks for the article! It's predicted only 10% of online activity this year will be human and the rest agentic. Two interesting articles come to mind here to understand and build safer frameworks around this:
1. Outlier ventures on their 'post web' thesis exploring how humans will only interact online on a residual part of the web reserved only for enriching and intentional interactions. https://outlierventures.io/postweb/
and
2. Gartners most recent report on how to balance the AI hype with internally implementing systems that are secure which we site in our most recent post here: https://innerworks2024.substack.com/p/openai-and-microsoft-accuse-deepseek?r=3z37ta