CISA vs CISM: What's Best for You?
Certification Focus, Job Roles and Salary Breakdown
The Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) and Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) certifications, both offered by ISACA, are among the most prestigious credentials in the cybersecurity and IT audit industries. Despite both being focused on information security, they cater to different professional areas. Understanding the distinctions between CISA and CISM is essential for professionals seeking to make the best decision for their career advancement.
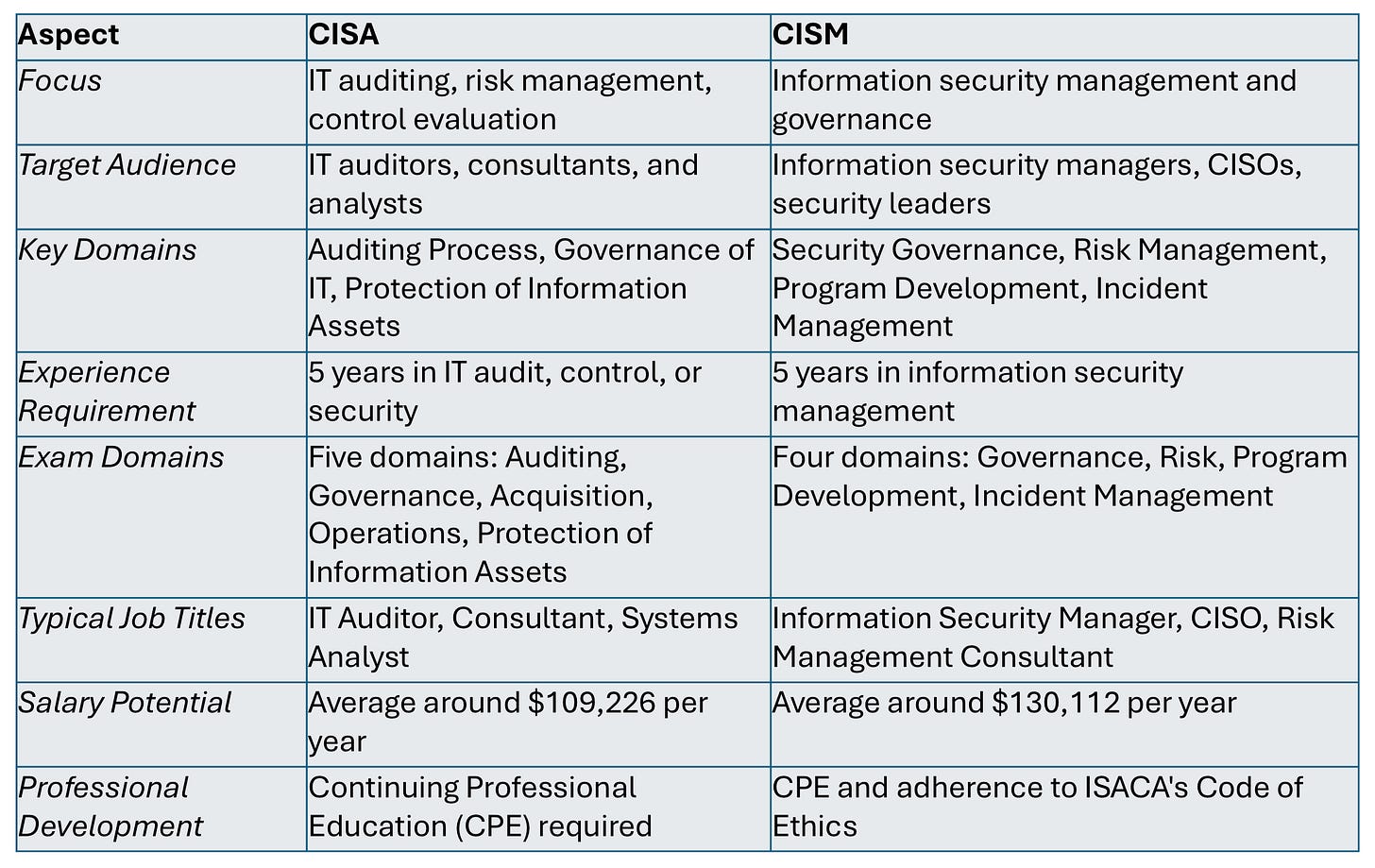
CISA is geared towards professionals who specialize in auditing, controlling, and monitoring IT systems. It is an auditing certification that helps professionals assess and manage the IT risk within an organization. CISA certification is best suited for IT auditors, consultants, and analysts whose job revolves around evaluating and auditing information systems, ensuring that they meet internal and external controls and compliance standards.
The exam for CISA is divided into five domains: Information Systems Auditing Process, Governance and Management of IT, Information Systems Acquisition, Development and Implementation, Information Systems Operations and Business Resilience, and Protection of Information Assets. These domains are focused on IT systems evaluation, risk management, and auditing, making the certification perfect for roles that require in-depth knowledge of IT audits and controls.
On the other hand, CISM is management-oriented, focusing on professionals tasked with overseeing an organization’s information security program. CISM certification prepares professionals for leadership roles, such as Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) or information security managers, who handle security governance, risk management, and the development of robust security programs aligned with business objectives.
CISM's exam focuses on four domains: Information Security Governance, Information Risk Management, Information Security Program Development and Management, and Information Security Incident Management. These domains emphasize high-level security governance, risk management, and strategic security management.
Both CISA and CISM certifications require five years of relevant work experience, but they emphasize different skill sets and career paths. CISA is more technical, focusing on evaluating the effectiveness of controls within IT environments, while CISM is more strategic, with a focus on managing the development and maintenance of security policies and practices at an organizational level. When choosing between the two, professionals should consider whether they prefer a technical audit and compliance role or a leadership role in managing information security.
CISM-certified professionals often have higher earning potential than those with CISA, reflecting the managerial nature of their roles. For example, the average salary for CISM holders tends to be slightly higher than CISA-certified professionals, given that CISM prepares individuals for executive-level positions.
In conclusion, both CISA and CISM are valuable certifications but cater to different professional needs. Those interested in IT auditing, risk management, and controls will benefit from CISA, while those focused on leading security programs and managing organizational risk will find CISM more aligned with their career objectives.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between the two certifications:
Ultimately, the decision between CISA and CISM should be based on your specific career goals and whether you are more interested in a hands-on audit role or a leadership position in managing security programs. Both certifications are valuable and highly regarded but offer different paths within the cybersecurity and IT industries.




As a holder of both CISA & CISM certifications, this is an excellent overview.
Well done!
I hold both CISA & CISM.
The CISA is a good preview of management roles. Having the audit background helps quite a bit in a CISM leadership role. 👍